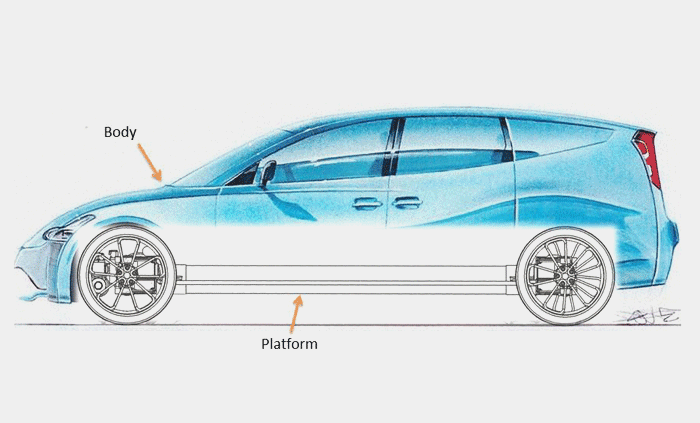
Platform
Ingocar
| |
US |
Metric |
| Weight Ingocar |
1.300 lbs. |
590 kg |
| Platform |
740 lbs. |
336 kg |
| Length, Width, Height - Wheelbase |
170” x 70” x 57” - 114" |
432 cm x 178 cm x 145 cm - 290 cm |
| Mileage |
190 MPG |
1,23 L/100km |
| Engine Power (Weight) |
40 hp (35 lbs.) |
30 kW (16 kg) |
| Accumulator |
1.6 MJ (36 hp•min) |
1,6 MJ (26.6 kW•min) |
| Wheel motors (4) |
485 hp (64 lbs.) |
356 kW (29 kg) |
| Speed (max.) |
100 mph |
160 km/h |
| Acceleration (0-62 mph) |
3 sec. |
3 sec. |
| Travel |
1,000 miles |
1.600 km |
| Trunk space (front / rear) |
22 cu ft. (7 / 15) |
620 Liter (200 / 420) |
| CO₂ Emissions (NEDC) |
33 gr/km |
33 gr/km |
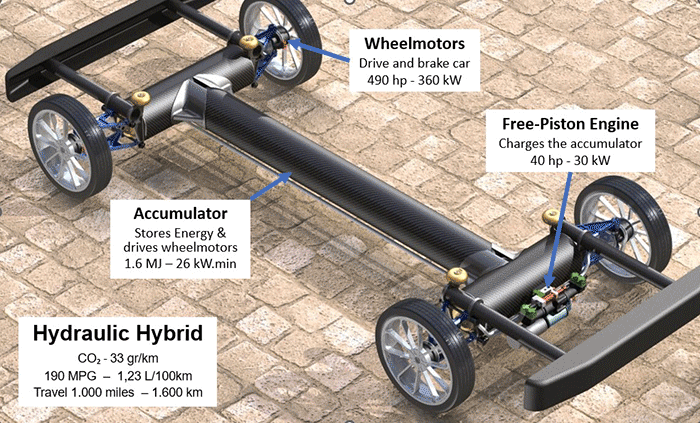
The Hydraulic Hybrid consists of the platform and car body. Both are manufactured independently from each other and are connected through four dampening elements during final assembly. Size and power of the platform are determined by the wheelbase, track, and total weight of the car independent on the type of body. Maintenance, repair, and model change-over are simplified and lower in costs.
The reductions in weight, fuel consumption and emissions are based on the low weight of the platform structure, the highly charged Hydraulic Free-Piston Engine (HFPE) operating only at constant speed and power, and the recuperation of the entire braking energy through the Hydraulic Wheel Motors (HWM). The energy is stored in the accumulator, the very stiff backbone of the car. The accumulator assembly withstands the high internal pressure and external forces from accidents without damage. The Ingocar is about 1.270 kg (2,800 lbs.) lighter than a BEV, and weighs 770 kg (1,700 lbs.) less than a conventional car, reducing the emissions during production and the costs.
The drivable platform includes active hydraulic bumpers at all four sides. They are automatically extended by the Platform Electronic Control Unit (PECU) by 60 cm (24") before a crash occurs and transfer the absorbed impact energy into the accumulator. The setting adjust automatically from ´soft´ for pedestrians to ´hard´ for larger objects and higher speeds. The side-bumpers are not shown in the renderings. The shock absorbers of the suspension and between platform and body are also controlled by the PECU to minimize undesirable body movements, like leaning and diving and the stiffness of the suspension.
Bursting of the very rigid accumulators through an accident is basically impossible due to the long distances of 60 cm (24") plus sections of the car body to absorb the crash energy. The partial release of non-flammable pressurized gas (Nitrogen) shortly before impact reduces the risk further.
The active hydraulic bumpers and an electronic control system of the vehicle allow for a cloud-controlled bumper-to-bumper traffic pattern, especially for heavy trucks, to increase safety and reduce fuel consumption, emissions and costs. The simple control of the hydrostatic drive, like speed, engine on-off, accumulator State of Charge (SOC), and movable bumpers for entering and leaving the train, support autonomous driving. In addition, the independent torque control of each wheel through the PECU enables ´torque-vectoring´ for improved stability and handling. The side-bumpers, not noticeable during entrance and exit of the car, are not shown for proprietary reasons.
Bumper in driving position
Bumper in position before impact
The HFPE and the hydraulic wheel motors (HWM) during braking pump fluid under high pressure with up to 450 bar (6,530 psi) into the accumulator by compressing the non-flammable Nitrogen gas which stores the energy. When reaching the desired SOC, the engine turns off automatically, and the fluid drives the wheel motors up to the desired speed, without shifting. For braking, the motors are reversed and pump the entire braking energy back into the accumulator. One charge is good for driving about 5 km (3.1 miles). The SOC is controlled by the PECU to provide always full capacity for acceleration or braking. Unlike electric batteries, super-capacitors, or fuel cells the accumulator has principally an unlimited life and maintains its full capacity also at very low and high temperatures.
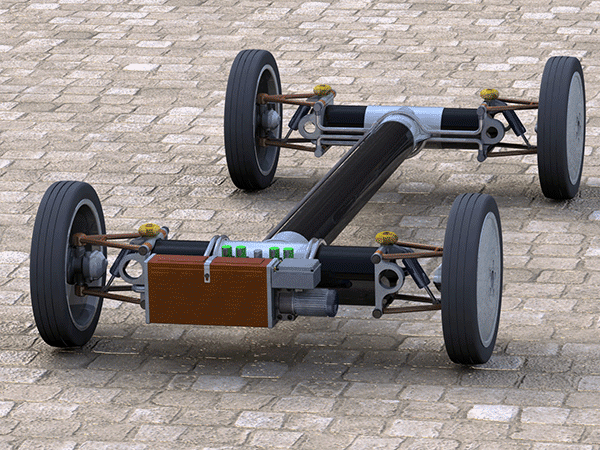 Electric-Hydraulic Module
Electric-Hydraulic Module
In addition, the Electric-Hydraulic Module (EH-Module) consisting of a battery, electric motor, and hydraulic pump for charging the accumulator can be simply attached to the front axle. The portable module weighs 52 kg (115 lbs.) and the battery 36 kg (80 lbs.) and allows for emission-free travel for up to 100 km (62 miles). However, the reduction in emissions is marginal when compared to the HFPE (Diesel) and non-existing when operating with Hydrogen.
Weight - Fuel Consumption - Emissions
The weight of the load-carrying car platform is based on CAD data and com-puter simulations from VTI, and that of the non-load carrying car body from reports from the Rocky Mountain Institute. (T.C. Moore, A.B. Lovins: Vehicle Design Strategies to Meet and Exceed PNGV Goals.)
HIGH MILEAGE AND LOW EMISSIONS THROUGH:
- Low vehicle weight of 590 kg (1,300 lbs.), a saving of 1.270 kg (2,800 lbs.) or 68% when compared with BEV's.
- Low fuel consumption of the HFPE (140 g/kWh | -32%) due to the high charge pressure and compression ratio (BMEP 35 bar +), reduced combustion heat losses through a ceramic coated combustion chamber (TBC) of compact size (surface -35%), and exhaust energy recuperation of pressure and heat through the Piston Impulse Charger & Compounder (PICC) and Rankine Cycle Unit (RCU).
- Recuperation of the entire braking energy. Savings: City 32%, NEDC 14%, Hwy 6%. (Argonne NL / SAE2013-01-1462 / NEDC = VTI)
- Low drag resistance. cw = 0.22, smooth underbody, narrow tires, small cooling surfaces, tapered rear (Rumpler type).
- Elimination of particulate matter (PM) from braking through the hydrostatic wheelmotors. The tire wear is reduced by 3/4 due to the low weight of the vehicle (-55%) and narrow tires.